Introduction to Spring Architecture
The Spring is having a well-organized architecture consisting of many modules. The following diagram represents the Spring Framework Architecture:
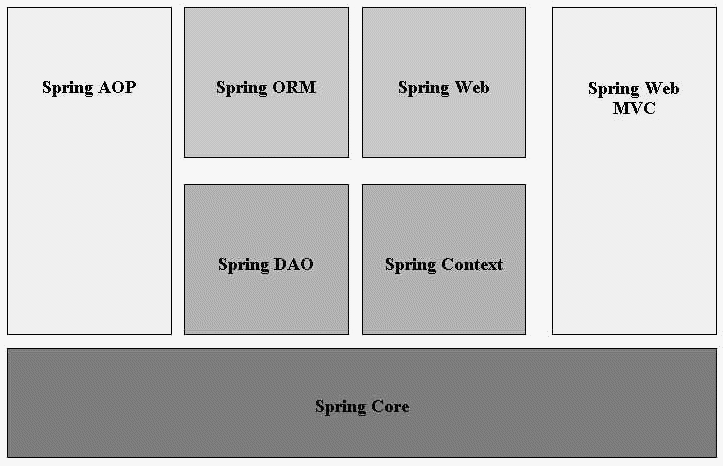
Figure 1: Spring Framework Architecture
The descriptions of the main modules in the Spring framework are given below:
1. Spring AOP
One of the key components of Spring is the AOP framework. AOP is used in Spring:
- To provide declarative enterprise services, especially as a replacement for EJB declarative services. The most important such service is declarative transaction management, which builds on Spring’s transaction abstraction.
- To allow users to implement custom aspects, complementing their use of OOP with AOP
2. Spring ORM
The ORM package is related to the database access. It provides integration layers for popular object-relational mapping APIs, including JDO, Hibernate and iBATIS.
3. Spring Web
The Spring Web module is part of Spring’s web application development stack, which includes Spring MVC.
4. Spring DAO
The DAO (Data Access Object) support in Spring is primarily for standardizing the data access work using the technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO.
5. Spring Context
This package builds on the beans package to add support for message sources and for the Observer design pattern, and the ability for application objects to obtain resources using a consistent API.
6. Spring Web MVC
This is the Module which provides the MVC implementations for the web applications.
7. Spring Core
The Core package is the most import component of the Spring Framework. This component provides the Dependency Injection features. The BeanFactory provides a factory pattern which separates the dependencies like initialization, creation and access of the objects from our actual program logic.